Search Coordinates
Overview
OsmAnd Coordinate search allows you to find a specific location by latitude and longitude. This type of search helps to identify a location accurately. It is especially useful for areas that do not have precise addresses, or for specific geographic tasks such as creating geo-fences or precise positioning in open space.
OsmAnd provides several ways to get to the Search tool → Address search tab, where the Coordinates search is located.
- The Search button on the map application screen.
- Go to the main Android Menu → Search → Address tab → Coordinates Search.
- When preparing to start a route, tap Navigation → Set destination → Search field → Address tab → Coordinates Search.
How to Use
- Android
- iOS
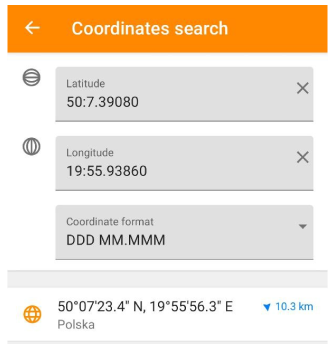
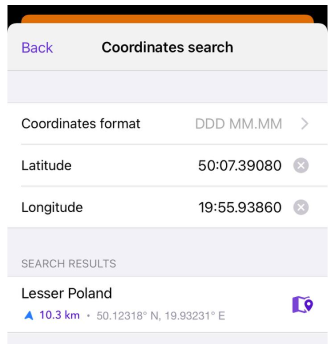
Coordinates can be entered in any available format, but the found location is displayed in the format specified in Configure profile → General settings → Units & formats.
- To use the coordinates search, you can type them in each corresponding field individually, or paste previously copied coordinates into the search field or enter them in it. The application prompts you to select a suitable location.
- Coordinate Search automatically converts one coordinate format to another when the specified format is changed in the field with their list.
- Tap the suggested location and the map context menu opens.
- More information can be found here Geographical coordinates.
Scope of the coordinate search function:
- Precise location. Coordinate search provides an accurate location. You can enter precise coordinates obtained, for example, from other sources such as a map, GPS device, or online services.
- Places without an address. Coordinates are particularly useful when it comes to places that do not have an exact address, or when the address is unknown. For example, it may be a remote area, a point on the sea, or a mountain peak. By entering coordinates, you can find and navigate to such locations without having to know the address.
- Location sharing. Searching by coordinates provides a convenient way to enter information. You can enter coordinates manually or copy them from other sources. This can be useful when sharing locations with others or using previously obtained coordinates.
Coordinate Format
There are several ways to enter coordinates for the search. To use each of them, it is very important to follow the input rules, otherwise the application will not be able to find the location.
-
DDD.DDDDD
Decimal coordinates (degrees). In this format, latitude and longitude coordinates are written in decimal format, for example, 52.37022° latitude and 4.89517° longitude for Amsterdam. This input method is easy to use and is the most common. You can read more about Decimal coordinates format here.
- Input rules. Latitude and longitude coordinates are written in decimal format, where latitude ranges from -90 to 90 and longitude ranges from -180 to 180.
- Most commonly used. Decimal coordinates are widely used in navigation applications, GPS devices, web maps, and other geo-positioning services.
-
DDD MM.MMM
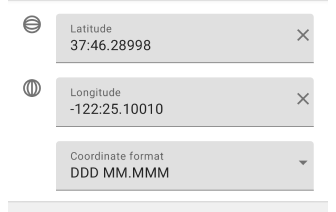
Degrees and Minutes(DM). In this format, latitude and longitude coordinates are recorded using degrees and minutes. For example, 37:46.29 latitude and -122:25.10 longitude for San Francisco. This format may be less accurate and may take longer to enter.
- Input rules. Latitude and longitude coordinates are written in a format that uses degrees (:) and minutes (:).
- Most commonly used. The DM format is often found in marine navigation, aviation, astronomy, and topographic mapping systems.
-
DDD MM SS.S
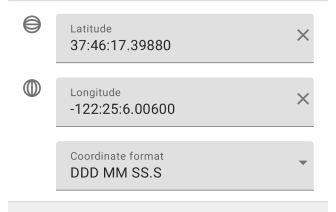
Degrees, Minutes and Seconds (DMS). The DMS coordinate format records geographic coordinates where values are given in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Degrees (DDD) can take values from 0 to 180 for longitude and 0 to 90 for latitude. Positive values indicate east longitude and north latitude, and negative values indicate west longitude and south latitude. Minutes (MM) can take values from 0 to 59. Seconds (SS.S) represent the decimal fraction of a second and can also range from 0 to 59.9.
- Input rules. Latitude and longitude coordinates are written in a format that uses degrees (:), minutes (:) and seconds (.).
- Most commonly used. The DMS format is widely used in geodesy, navigation applications, cartography, astronomy, and other fields where a more detailed expression of location coordinates is required.
-
UTM Standard
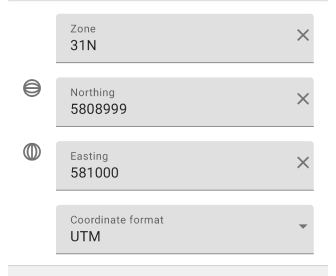
UTM (Universal Transversal Mercator System). In this format, coordinates are specified using UTM zone, East and North directions. For example, for Amsterdam, the coordinates might be approximately as follows: zone 31, East direction 581000, North direction 5809000. Entering coordinates in UTM format may require some familiarity with the system and be more complex than other formats, but it provides good accuracy and meets global geo-positioning standards. You can read more about the UTM format here.
- Input Rules. Coordinates are recorded in a format that uses the UTM zone and Eastern and Northern offsets.
- Most commonly used. UTM format is often used in surveying, mapping, and geographic information systems for measurement and navigation.
-
Open Location Code ((OLC) - 9F2X4WFJ+7W (Open Location Code represents area 9m x 14m))
Open Location Code (OLC), also known as Plus Code, is a global location coding system. It is a combination of letters and numbers to indicate the latitude and longitude of any location on the planet. Example of an OLC code for Amsterdam: 9F3WCVWG+FP. In this example, "9F3WCVWG" indicates a coarse grid, and "+FP" specifies a location within that area. Read more here.
- Input Rules.
- The OLC code consists of 4 to 14 characters, which can be letters from "C" to "Z" (except for "I" and "O") and numbers from "2" to "9".
- The code begins with a global prefix that indicates a continent or area.
- This is followed by groups of characters that are separated by dots. Each group represents a narrower area.
- To clarify the location, letters and digits are supplemented by other characters in the OLC code.
- Most commonly used. OLC is often used in areas where precise addresses are not available or are difficult to determine, such as remote areas, deserts, or oceans. It is also widely used in applications and services related to geo-positioning, delivery, emergency services, and other areas where precise location is required without the use of traditional addresses.
- Input Rules.
-
MGRS
MGRS (Military Grid Reference System). This is a coordinate system often used in military applications. It is based on the UTM system and is supplemented with an additional grid of squares. An example of coordinates in MGRS format for a location in Australia can be as follows: 55HBE1234567890. In this example, "55H" represents the MGRS zone and "BE" represents the square in which the location is located. "123456" represents the eastward offset and "7890" represents the northward offset within that square. MGRS are widely used in areas requiring high accuracy and geo-referencing. They are particularly useful in environments where addresses may not be clear or available, such as military operations or expeditions in remote areas. You can read more about the MGRS format here.
- Input rules. The coordinates consist of an MGRS zone, a square, and two more digits indicating east and north offsets.
- Most commonly used. The MGRS format is widely used in military navigation and communications, and can also be useful for outdoor enthusiasts and hikers.
-
Swiss Grid (CH1903) and Swiss Grid (CH1903+)
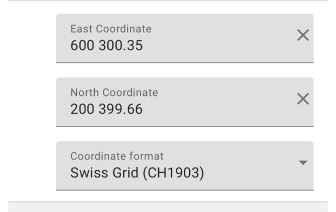
Swiss coordinate system. Swiss Grid (CH1903) and Swiss Grid (CH1903+) are coordinate systems widely used in Switzerland for positioning. Both formats are based on the CH1903 system, which was introduced in 1903 and is based on the projection of the Swiss International Grid. Example coordinates in Swiss Grid (CH1903) format — Eastern: 600000; Northern: 200000. In Swiss Grid (CH1903+) format — Eastern: 600300; Northern: 200400. You can read more about the Swiss Grid geographic coordinate system here.
- Input rules.
- Coordinates in CH1903 format consist of two components: Eastern and Northern.
- Eastern is in meters from a point called the Lucerne Axis (zero Eastern).
- Northern is given in meters from the equator.
- The CH1903+ format uses the same input rules as CH1903, but with more precise values.
- CH1903+ includes corrections to account for shifts in coordinates caused by changes in tectonic movements in Switzerland.
- Most commonly used. The Swiss Grid (CH1903) and Swiss Grid (CH1903+) formats are used in Switzerland for geodetic measurements, cartography, geographic information systems, and construction and engineering. These formats provide a local coordinate system specific to Switzerland.
- Input rules.
For each profile separately you can set a different coordinate format. To do this, go to General settings → Coordinate format.